Understanding your customer is essential for business growth. Today’s buyers interact with brands on many channels, creating a complex web of touchpoints. Without clarity, businesses risk losing sales and loyal customers. A customer journey map helps visualize interactions, showing key steps, challenges, and emotions customers experience.
This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about customer journey mapping. You’ll discover its definition, importance, benefits, and types, and learn how to create a journey map using clear, actionable steps. Real-world examples and tool recommendations help you get started. You’ll also find common mistakes to avoid, best practices, and insights on future trends. By following this guide, you can design effective journey maps to improve satisfaction, boost conversion rates, and foster brand loyalty. Key takeaways: Learn what customer journey mapping is, how to create one, what tools to use, common pitfalls to avoid, and strategies for long-term success.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map visually shows the path a customer takes with a brand, from awareness through purchase and post-purchase. It highlights actions, emotions, motivations, and obstacles, giving a holistic view from the customer’s perspective.
Unlike traditional sales funnels that focus only on conversion, journey maps provide insights into customer emotions and experiences at every stage. This allows for the identification of both positive and negative moments, making it easier to optimize each touchpoint and boost customer satisfaction. For instance, if an eCommerce business faces high checkout abandonment rates, a journey map can pinpoint whether the issue stems from confusing payment options, unclear shipping costs, or slow page load times. Understanding these details enables brands to make informed improvements, which ultimately enhance the customer experience. Key takeaway: Journey mapping highlights the root causes of friction, helping brands act effectively.
Furthermore, journey mapping encourages companies to think beyond transactions and fosters long-term customer relationships. It serves as a blueprint for aligning teams and designing strategies that genuinely meet customer needs while increasing loyalty and advocacy.
Why Customer Journey Mapping Matters
Customer journey mapping is more than a marketing exercise—it’s a strategic tool that drives business growth and competitive advantage. One of the key reasons it matters is that it uncovers hidden friction points that might otherwise go unnoticed. For example, slow customer support response times or confusing website navigation can frustrate buyers and lead to abandonment. Identifying these friction points allows businesses to proactively improve the overall experience.
Another reason journey mapping is critical is that it fosters collaboration across departments. Marketing, sales, product, and customer support teams often operate in silos, but a journey map provides a shared understanding of the customer experience. This alignment ensures that every department works toward a common goal: delivering a seamless, positive experience at every touchpoint.
Customer journey mapping also enhances personalization. Customers expect brands to anticipate their needs. By analyzing behaviors and pain points, companies can deliver timely, relevant messages and offers.
Finally, journey mapping directly impacts revenue. Improved experiences increase conversion rates, reduce churn, and enhance customer lifetime value. Brands that fail to invest in understanding the customer journey risk losing market share to competitors who are more attuned to their audience’s needs.
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping delivers measurable benefits across marketing, sales, and customer experience teams. First, it gives businesses a comprehensive understanding of their customers’ behavior. By combining quantitative data, such as website analytics, with qualitative insights from surveys and interviews, companies gain a nuanced view of both actions and motivations.
Second, journey mapping improves conversion rates. Identifying friction points allows brands to remove obstacles in the buying process, resulting in smoother experiences that drive purchases. For instance, if users abandon an online checkout due to confusing shipping options, simplifying the process can significantly boost conversions.
Journey mapping boosts retention and loyalty. By meeting customer expectations, companies can offer proactive solutions and personalized support, creating satisfied repeat buyers.
Journey mapping guides effective marketing. Brands can focus on top touchpoints and targeted messaging to increase ROI and minimize wasted spend.
Together, these benefits highlight why customer journey mapping is indispensable for modern businesses. To gain these advantages, it’s important to understand the necessary elements of a robust customer journey map.
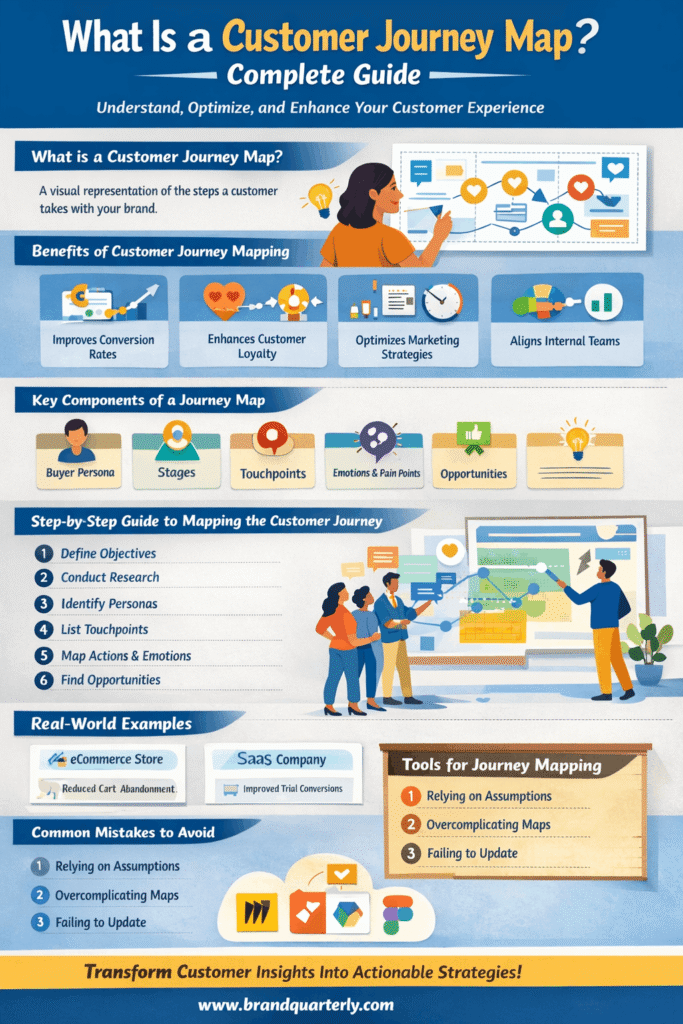
Key Components of a Customer Journey Map
A high-quality customer journey map includes several critical components that ensure a complete understanding of the customer experience.
Buyer Persona
The journey starts with a well-defined buyer persona that represents a segment of your target audience. Personas include demographic details, behaviors, goals, challenges, and preferences. They help ensure the map is based on real customer experience rather than assumptions. Without a clear persona, businesses risk generic maps that lack actionable insight.
Customer Stages
Customer stages break the journey into phases such as Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy. This framework helps companies understand customer progression and obstacles. By analyzing each stage, teams can tailor strategies to improve the experience and conversion rates and assign responsibilities for each part of the journey.
Touchpoints
Touchpoints are the various interactions a customer has with your brand. These include digital channels such as websites, emails, and social media, as well as offline channels such as in-store visits and phone support. Mapping touchpoints helps businesses identify areas that positively or negatively influence the customer experience. Every touchpoint can be an opportunity to impress or a risk of friction, so mapping them all ensures nothing is overlooked.
Customer Actions, Emotions, and Pain Points
Mapping customer actions shows what happens at each stage, like searching for reviews, signing up for newsletters, or contacting support. Recording emotions—whether excited, frustrated, or confused—adds context. Identifying pain points highlights where improvements can enhance satisfaction. Understanding this emotional journey helps design experiences that resonate.
Opportunities
Finally, journey maps identify opportunities for improvement, such as streamlining onboarding, clarifying messaging, or enhancing support. These insights help businesses prioritize initiatives with the greatest impact on the customer experience. Opportunities may also involve personalization, automation, or omnichannel integration to make the journey seamless.
Types of Customer Journey Maps
To choose the right map for your objectives, it’s important to understand the options available. Let’s review the main types of journey maps and the scenarios where each is most effective.
Current State Journey Map
A current state map visualizes how customers interact with your brand today. It focuses on existing experiences, identifies pain points, and reveals areas requiring immediate improvement. By understanding the current journey, businesses can make informed, data-driven optimizations. Current-state maps are especially useful for addressing friction and reducing churn.
Future State Journey Map
A future state map represents the ideal experience a business wants customers to have. It is often used during digital transformation, product redesigns, or rebranding initiatives. Future state maps encourage innovation and help teams plan improvements proactively. They act as a roadmap for long-term experience enhancements and strategic investments.
Day-in-the-Life Journey Map
A day-in-the-life map explores a customer’s daily activities beyond brand interactions. It provides context for understanding broader motivations, habits, and pain points that affect purchasing decisions. This type of map is particularly useful for lifestyle brands and service industries. By understanding customers’ routines, companies can design experiences that fit naturally into their lives.
Service Blueprint
A service blueprint extends the journey map by incorporating internal processes, systems, and team responsibilities. It links front-end customer experiences to back-end operations, ensuring that internal workflows align with customer needs. Service blueprints help identify inefficiencies in internal processes that may indirectly affect the customer experience.
Segment-Specific Journey Map
A segment-specific map focuses on a particular persona or customer segment. It highlights how experiences differ across demographics, behavior patterns, or usage scenarios. This granularity allows businesses to create targeted improvements that resonate with specific audiences and tailor campaigns for maximum impact.
Creating a Customer Journey Map: Detailed Instructions
Creating a journey map involves structured research, collaboration, and careful analysis.
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Start by clarifying the purpose of the journey map. Are you aiming to reduce churn, improve onboarding, increase conversions, or enhance customer support? A clearly defined objective keeps the project focused and ensures that insights are actionable. Clear objectives also help in prioritizing which touchpoints or stages need the most attention.
Step 2: Conduct Customer Research
Collect data from multiple sources, including surveys, interviews, website analytics, social media monitoring, and customer support logs. Using real data ensures accuracy and prevents assumptions that can skew the map. Listening to customers directly uncovers insights that internal teams may overlook, giving a holistic view of behavior and sentiment.
Step 3: Identify Personas
Segment your audience and select one persona at a time to map. Attempting to map multiple personas simultaneously can dilute insights and create confusion. Focused personas allow for precise analysis of behaviors, goals, and motivations. They also help in crafting targeted experiences for different segments of your audience.
Step 4: List Touchpoints
Document every possible interaction your customers have with your brand. Include digital touchpoints like emails, website visits, and social media, as well as offline touchpoints like phone calls, in-store visits, and events. Each touchpoint can influence customer perception and satisfaction. Mapping them ensures no interaction is overlooked.
Step 5: Map Actions, Emotions, and Pain Points
Outline what customers do, how they feel, and what obstacles they face at each stage. Emotional insights are critical because they indicate where customers are delighted or frustrated. Mapping these experiences allows brands to prioritize improvements effectively. It also provides a reference for internal teams to design empathetic solutions.
Step 6: Identify Opportunities
Analyze pain points and emotional lows to determine opportunities for improvement. Opportunities may involve simplifying processes, enhancing support, personalizing messaging, or introducing automation. Prioritize changes with the greatest impact on satisfaction, retention, and conversion rates.
Step 7: Validate With Teams
Share your draft map with teams across marketing, sales, product, and support. Collaboration ensures that insights are accurate, actionable, and aligned with internal processes. Feedback also helps identify blind spots that may have been overlooked during research. Team validation increases map adoption across departments.
Step 8: Implement and Monitor
Apply insights to optimize processes, touchpoints, and communications. Track KPIs regularly to measure the effectiveness of changes. A journey map is a living document that should be updated as customer behaviors evolve. Regular monitoring ensures your strategy stays aligned with real-world needs.
Real-World Examples of Customer Journey Maps
Example 1: eCommerce Brand
A fashion retailer mapped a customer’s journey from social media discovery to repeat purchases. In the Awareness stage, customers encountered Instagram ads and influencer posts. During Consideration, they browsed product pages, checked reviews, and compared alternatives. At the Decision stage, many abandoned carts due to confusion about shipping costs, prompting the brand to simplify pricing information and offer free shipping options. Post-purchase, personalized thank-you emails and loyalty programs encouraged repeat purchases, increasing overall customer lifetime value.
Example 2: SaaS Company
A software provider mapped the journey from free trial sign-ups to paid subscriptions. Customers discovered the brand through paid search and content marketing, then engaged with a free trial. Many trial users dropped off due to unclear onboarding instructions, revealing a pain point. The company introduced interactive tutorials and proactive email guidance, improving conversion rates from trial to paid users. Post-purchase engagement included webinars, in-app support, and personalized tips, boosting retention and significantly reducing churn.
Tools for Creating a Customer Journey Map
Several digital tools simplify journey mapping for teams of all sizes. Miro offers collaborative whiteboards and templates for visualizing journeys. Lucidchart provides diagramming tools for creating detailed journey maps with multiple layers. UXPressia specializes in journey-mapping software that tracks personas, touchpoints, and KPIs. Figma is useful for creating visually appealing maps and integrating design and research workflows. Traditional tools like Microsoft Visio are also effective for complex maps and internal documentation. Even simple spreadsheets can work if backed by solid customer research and analysis.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes is relying on assumptions rather than real customer data. Internal opinions rarely reflect actual behavior, and incorrect assumptions can lead to misguided strategies. Another mistake is overcomplicating the journey map with excessive detail, making it difficult to interpret or act on.
Failing to update the map regularly is another frequent error. Customer behaviors, technology, and market conditions change over time, so a static map quickly becomes outdated. Finally, some organizations create journey maps but fail to implement the insights they yield. Without action, journey mapping becomes a decorative exercise with no impact on the customer experience or business results.
Best Practices for Effective Journey Mapping
Involve cross-functional teams from marketing, sales, product, and support to enrich the mapping process. Keeping the customer at the center of every decision ensures that strategies are empathetic and effective. Combine quantitative and qualitative data to capture both what customers do and why they behave the way they do.
Continuously test, monitor, and refine the journey map. Customer experiences are dynamic, and ongoing updates ensure your map reflects reality. Prioritize actionable insights over aesthetic perfection, focusing on changes that drive measurable improvements. Finally, document and share the journey map with the organization to foster alignment and collaboration across departments.
Measuring the Success of a Journey Map
Measuring the impact of a journey map involves tracking specific KPIs. Key metrics include conversion rates at each stage, customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), net promoter scores (NPS), churn rates, and lifetime value. Engagement metrics such as website clicks, email opens, and social media interactions also provide valuable insights. Regularly reviewing these KPIs ensures that the map informs actionable improvements and delivers measurable ROI.
How Customer Journey Mapping Improves ROI
Customer journey mapping directly contributes to business growth. By identifying friction points, companies reduce drop-offs and increase conversions. Improved experiences foster customer loyalty, leading to repeat purchases and higher lifetime value. Marketing efforts become more targeted, reducing wasted spend and improving campaign ROI. Alignment of internal processes around the journey also boosts operational efficiency, reducing duplication and errors. Finally, satisfied customers are more likely to advocate for the brand, generating organic referrals and lowering acquisition costs.
Future Trends in Customer Journey Mapping
AI-powered insights are shaping the future of journey mapping, enabling predictive analytics that anticipate customer behavior. Omnichannel integration will create seamless experiences across digital and offline channels, ensuring consistency. Real-time journey tracking will allow brands to respond immediately to changing customer needs. Emotional analytics will become more prominent, measuring customer sentiment through voice, text, and facial cues to better understand emotional drivers. These trends suggest that journey mapping will evolve from a static planning tool to a dynamic, real-time strategy for customer experience optimization.
Final Thoughts
A customer journey map is more than a visual diagram; it is a strategic framework for understanding, optimizing, and enhancing every interaction a customer has with your brand. By mapping the customer experience, organizations can improve satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue while streamlining internal processes.
Investing in journey mapping ensures that businesses align teams around the customer, uncover hidden pain points, and identify opportunities for growth. In today’s competitive marketplace, companies that understand their customers’ journeys gain a significant advantage. Implementing a well-researched, actionable journey map transforms customer experience into a sustainable growth engine and strengthens long-term brand relationships.
